DFB Laser
Understanding the Principles of DFB Lasers
A Distributed Feedback (DFB) laser is a type of semiconductor laser commonly used in telecommunications, sensing, and other precision optical applications. Its distinct feature lies in its ability to provide stable, single-wavelength output with minimal spectral linewidth. This capability is achieved through its unique design and operating principles.
Structure of a DFB Laser
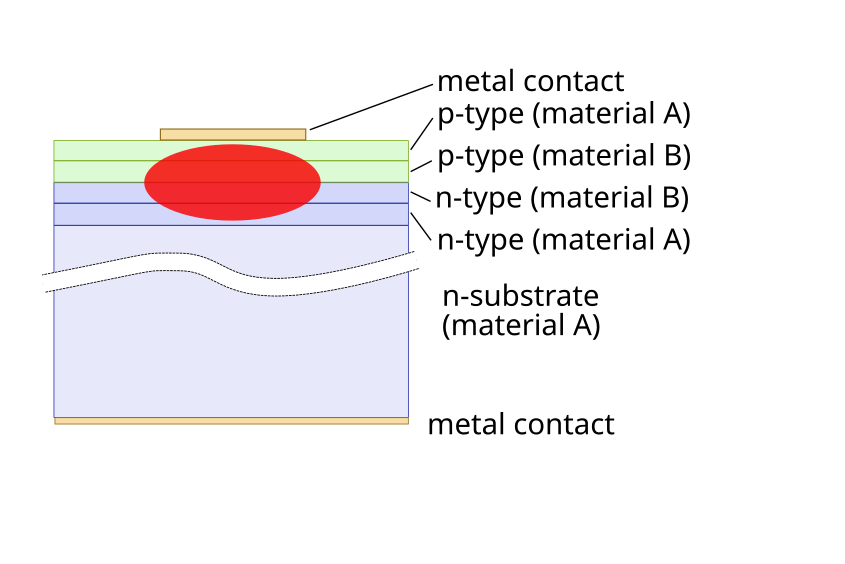
A DFB laser consists of several key components:
- Active Region: This is where the optical gain is generated when the semiconductor material is electrically pumped.
- Bragg Grating: A periodic structure within the laser's waveguide that acts as a wavelength-selective element. It reflects specific wavelengths of light and allows others to propagate.
- Waveguide: The channel through which light is confined and guided.
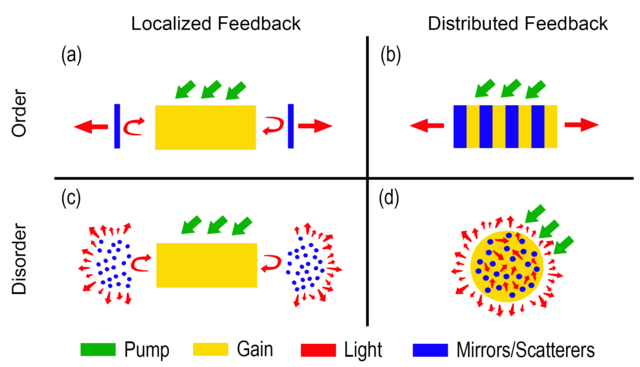
Unlike Fabry-Pérot (FP) lasers, which use reflective facets at their ends to form a cavity, DFB lasers incorporate the Bragg grating along the active region. This structure eliminates the need for highly reflective end facets and provides wavelength selectivity along the laser's length.
Operating Principle
The DFB laser relies on the principle of distributed feedback to select and amplify a specific wavelength:
Optical Gain and Feedback:
- When current is applied to the active region, electrons and holes recombine to produce photons.
- The Bragg grating reflects a narrow range of wavelengths back into the active region while other wavelengths pass through or are attenuated.
Single-Mode Operation:
- The Bragg grating's periodicity determines the specific wavelength (Bragg wavelength) that experiences constructive interference and strong feedback.
- This ensures that the DFB laser operates predominantly in a single longitudinal mode, with minimal side modes.
Stability and Linewidth:
- The distributed feedback mechanism ensures that the emitted wavelength remains stable even under temperature and current variations.
This stability is crucial for applications like optical communication, where precise wavelength control is essential.
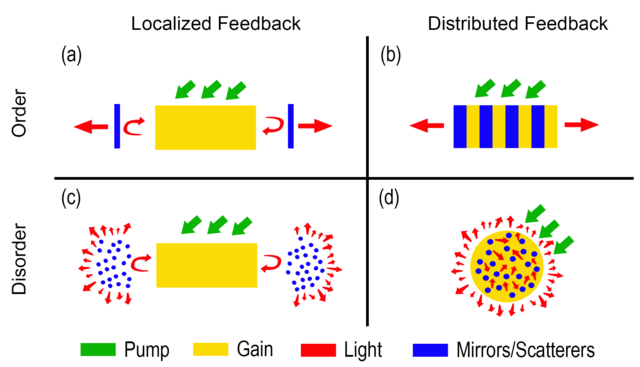
Image by The Photon, licensed under the GNU Free Documentation License. You can freely copy, distribute, and modify it under the terms of the license. Full license information available at https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/Commons:GNU_Free_Documentation_License,_version_1.2.
Advantages of DFB Lasers
- Narrow Linewidth: The single-mode operation minimizes spectral linewidth, enabling high signal fidelity.
- Wavelength Stability: The integration of the Bragg grating ensures that the output wavelength is less sensitive to external perturbations.
- Low Threshold Current: The design reduces energy loss, resulting in efficient lasing at lower currents.
- Compatibility with Fiber Optics: DFB lasers are ideal for coupling with optical fibers, making them indispensable in telecommunications.
Applications
DFB lasers find applications in various fields, such as:
- Telecommunications: High-speed data transmission over fiber-optic networks.
- Spectroscopy: Precision measurements of gas absorption and molecular composition.
- Sensing: Detection of environmental changes, such as temperature and pressure, through wavelength shifts.
- Lidar: Accurate distance measurement and 3D mapping in autonomous vehicles.
Conclusion
DFB lasers represent a significant advancement in semiconductor laser technology, providing unparalleled stability and precision. Their unique structure, incorporating a Bragg grating for wavelength selection, makes them indispensable in applications requiring high-performance optical sources.
 TO Packages
TO Packages
 Semiconductor Laser
Semiconductor Laser
 DFB Laser
DFB Laser
 LiDAR Technology
LiDAR Technology
